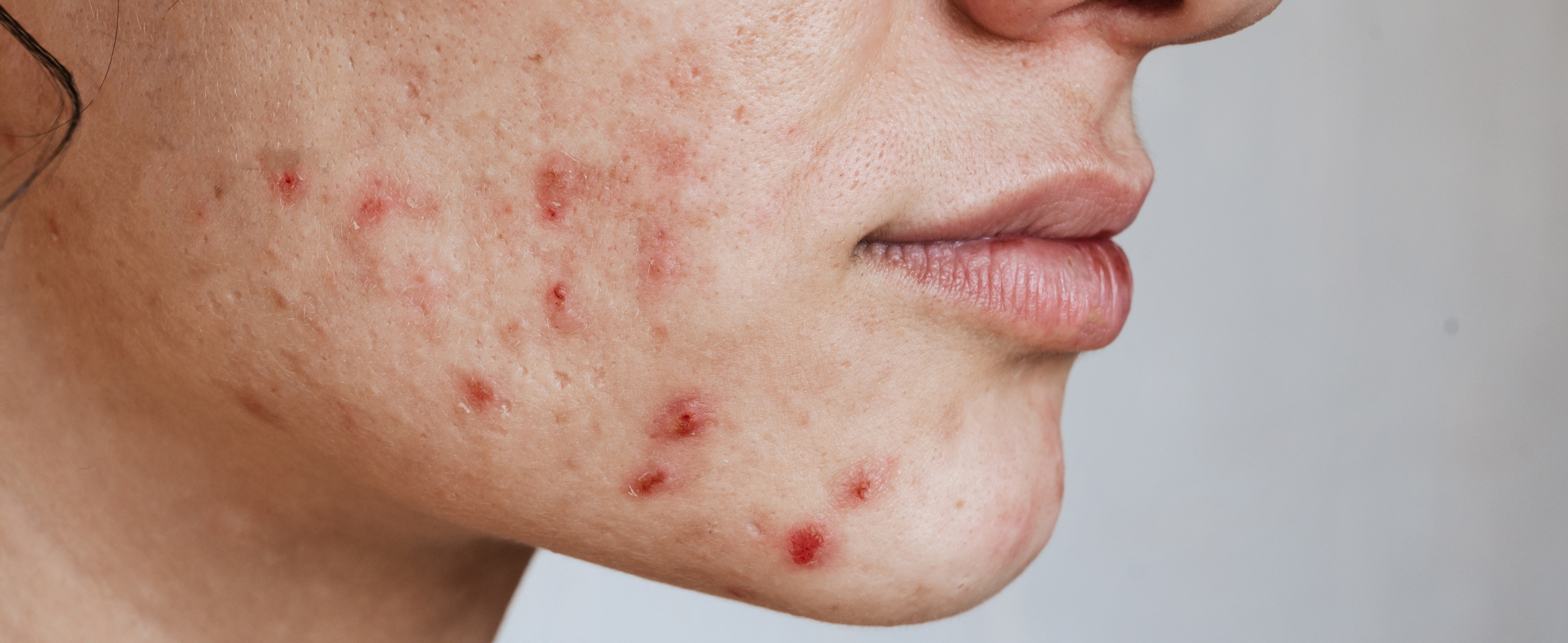
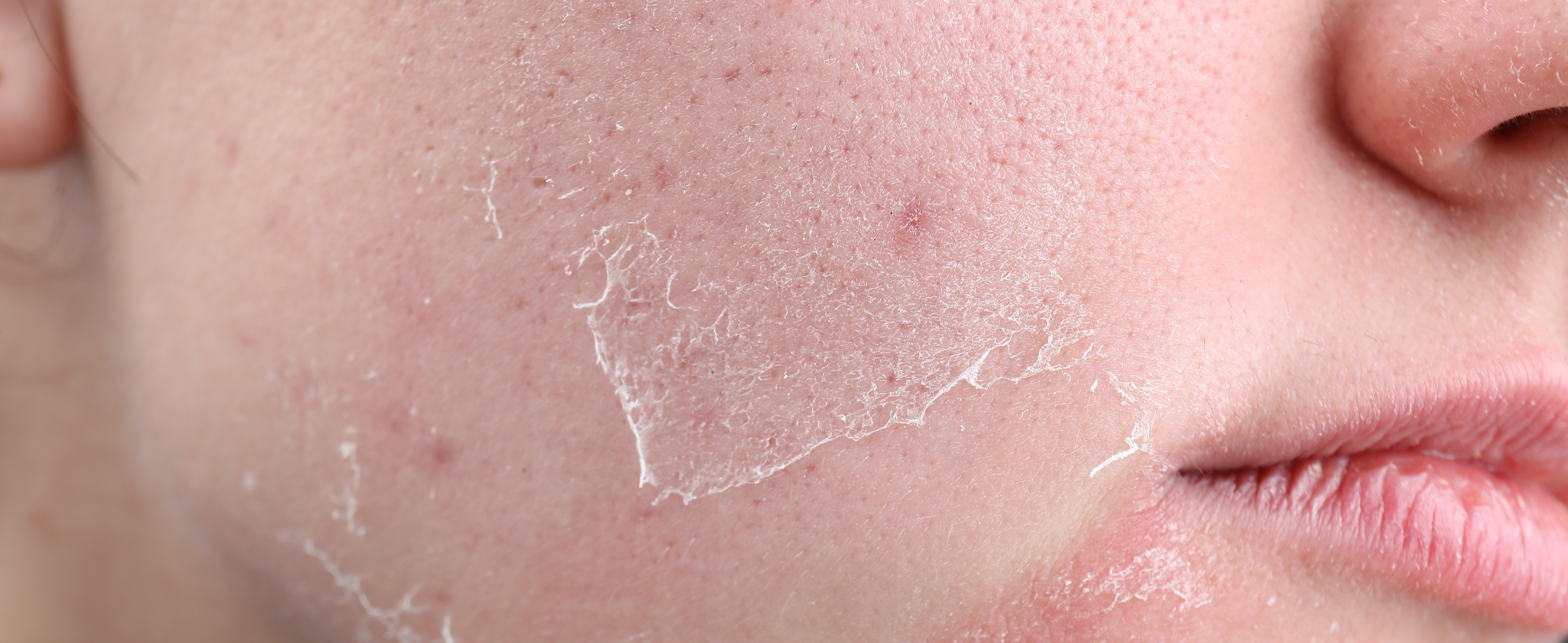
Acne is one of the most common skin concerns, affecting millions of people worldwide. From stubborn blackheads to painful cystic breakouts, finding an effective treatment can be a frustrating process. Retinol, a derivative of Vitamin A, has gained widespread attention as a powerful acne-fighting ingredient. But does it really work? Let’s explore how retinol helps with acne, unclogs pores, and reduces breakouts to determine if it’s the right solution for you.
How Retinol Works for Acne
Retinol is a form of retinoid, which is known for its ability to accelerate skin cell turnover and prevent clogged pores. When applied to the skin, retinol works in several ways to combat acne:
1. Unclogging Pores
Acne often occurs when dead skin cells and excess oil accumulate in the pores, leading to blockages and bacterial growth. Retinol helps by exfoliating the skin at a deeper level, promoting the shedding of dead skin cells, and preventing clogged pores. This action reduces the formation of blackheads and whiteheads, keeping the skin clearer over time.
2. Regulating Oil Production
Excess sebum (oil) production is a major factor in acne development. Retinol helps regulate oil production by balancing the skin’s natural sebum levels. By controlling excess oil, retinol minimizes the risk of pores becoming clogged and forming acne lesions.
3. Reducing Inflammation
Inflammation plays a key role in acne, leading to red, swollen, and painful breakouts. Retinol has anti-inflammatory properties that help calm the skin and reduce the severity of active acne. Over time, this can result in a smoother and more even complexion.
4. Stimulating Cell Turnover
One of the primary benefits of retinol is its ability to speed up the skin’s natural cell turnover process. This means that new, healthy skin cells replace older, damaged ones more quickly, reducing the appearance of acne scars and preventing new breakouts from forming.
5. Boosting Collagen Production
While acne primarily affects the skin’s surface, it can also damage deeper layers, leading to scarring. Retinol stimulates collagen production, which helps repair and strengthen the skin’s structure. Over time, this can improve skin texture and fade post-acne marks.
How to Use Retinol for Acne Effectively
Although retinol is a powerful ingredient, using it correctly is crucial to achieving the best results while minimizing potential side effects. Here’s how to incorporate retinol into your acne-fighting skincare routine:
1. Start with a Low Concentration
Retinol can be potent, and using a high concentration right away may cause irritation. Beginners should start with a lower-strength formula (0.1% to 0.3%) and gradually increase as their skin builds tolerance.
2. Apply at Night
Retinol is best applied in the evening because it can make the skin more sensitive to sunlight. Nighttime application allows retinol to work without interference from UV exposure.
3. Use a Pea-Sized Amount
A little goes a long way with retinol. Apply a small, pea-sized amount to clean, dry skin, focusing on areas prone to breakouts. Avoid applying it too close to the eyes or mouth, as these areas are more sensitive.
4. Moisturize to Prevent Dryness
One of the most common side effects of retinol is dryness and peeling. To prevent this, follow up with a gentle, hydrating moisturizer to keep the skin balanced and comfortable.
5. Be Patient and Consistent
Results from retinol take time. It may take 6 to 12 weeks before noticeable improvements in acne and skin texture occur. Consistency is key—stick to your routine and resist the temptation to use more product in hopes of faster results.
6. Always Wear Sunscreen
Since retinol increases the skin’s sensitivity to sunlight, applying a broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher) every morning is essential. This helps prevent sun damage and protects the skin while using retinol.
Potential Side Effects and How to Manage Them
While retinol is highly effective for treating acne, it can also cause side effects, especially in the initial stages of use. Common side effects include:
- Dryness and Peeling: Use a gentle moisturizer and avoid over-exfoliating.
- Redness and Irritation: Reduce application frequency (e.g., every other night) until your skin adjusts.
- Purging: Some users experience an initial breakout as clogged pores come to the surface. This is temporary and usually subsides within a few weeks.
If side effects persist or become severe, consider consulting a dermatologist for personalized advice.
Who Should Use Retinol for Acne?
Retinol can be beneficial for many people struggling with acne, but it’s especially helpful for those dealing with:
- Mild to moderate acne (blackheads, whiteheads, and small pimples)
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (dark spots left by acne)
- Uneven skin texture or enlarged pores
- Early signs of aging alongside acne-prone skin
However, individuals with extremely sensitive skin, severe cystic acne, or conditions like eczema or rosacea should consult a dermatologist before using retinol.
Is Retinol the Right Choice for Acne?
The short answer is: yes, retinol can be highly effective for treating acne. By unclogging pores, regulating oil production, and reducing inflammation, retinol helps prevent breakouts and improves overall skin texture. However, patience and proper usage are key to seeing long-term results.
If you’re struggling with persistent acne and haven’t tried retinol yet, it may be worth incorporating into your skincare routine. Just remember to start slow, stay consistent, and always protect your skin with sunscreen. With time and the right approach, retinol can be a game-changer for clearer, healthier skin.